MATLAB MCP Client is out on GitHub now!
 |
Guest Writer: Shweta Pujari Shweta Pujari is the Product Manager for AI and GenAI. In this blog post, she joins me to demonstrate how to use the new MATLAB MCP Client to build agentic workflows in the MATLAB language. |
What is the MATLAB MCP Client?
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an emerging standard that defines how AI models communicate with external tools and services. Think of MCP as a language that both an AI model and a tool server understand – it covers how to list what tools are available and how to invoke those tools with specific inputs, getting back results in a structured way. Many advanced LLM applications today use agents that can call external functions (for example, an AI assistant that calls a weather API or database query). MCP provides a formal framework for this kind of tool calling so that any AI client can talk to any tool server that speaks MCP. With this capability, you can implement an MCP client entirely in MATLAB code. In practical terms, this add-on allows MATLAB to connect to an MCP-compatible server over HTTP and use the tools that server offers. Once connected, MATLAB can list the available tools on that server and then call those tools on demand. Importantly, this integration is designed to work hand-in-hand with the Large Language Models (LLMs) with MATLAB add-on, enabling the language model to automatically decide when to use these tools as needed.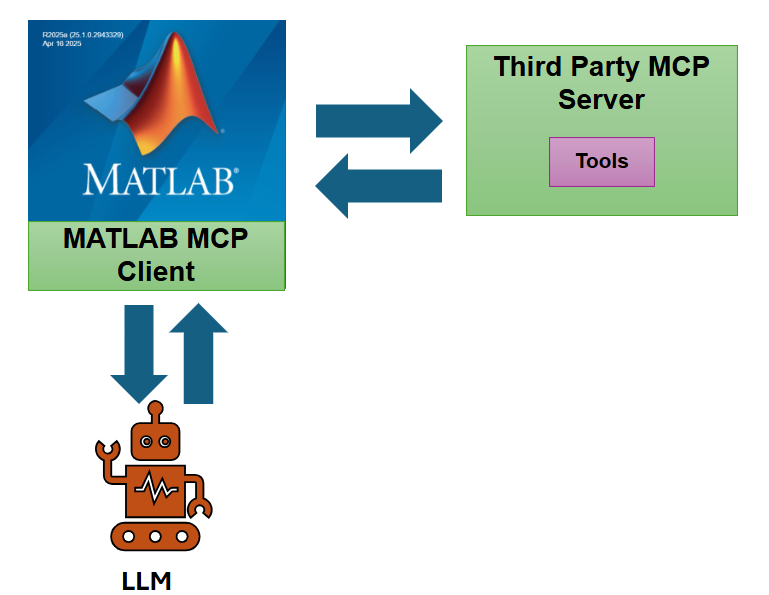
Key capabilities of the MATLAB MCP Client
- Connecting to Tools via MCP Servers: You can create an MCP client in MATLAB that connects to any streamable HTTP MCP server by specifying its URL (endpoint). Upon connection, the client automatically fetches the list of available tools from the server. This means MATLAB instantly knows what functions the server can perform (e.g., “get_weather”, “run_simulation”, “query_database”, etc.), along with details about each tool’s inputs and outputs.
- Calling External Tools: With the MCP client, calling an external tool becomes as straightforward as calling a local MATLAB function. The add-on provides a high-level function callTool for this purpose. You simply pass in the tool name and required parameters, and callTool handles the communication with the server, returning the result to MATLAB. There’s no need to manually craft HTTP requests or parse JSON – the client does that behind the scenes. This dramatically simplifies integration with external APIs or services.
- Integrating with LLM Workflows: Perhaps the most exciting capability is enabling “agentic” AI workflows. By combining this MCP client with the LLMs with MATLAB add-on, you allow a large language model in MATLAB to autonomously decide when to call an external tool to fulfill a user’s request. The MCP client exposes the server’s tools to the LLM: you convert the list of tools into a form the model understands (openAIFunction objects for OpenAI’s function-calling interface) and pass them into your LLM session. Then, when you prompt the LLM, it can choose to output a tool call (including the tool name and arguments) if it determines that using a tool is the best way to get the answer. MATLAB captures this intended function call, and you can execute it via callTool(client, toolRequest) to get the result. In short, the MCP client makes it possible for an AI assistant in MATLAB to not just talk about external data or actions, but to actually perform those actions by invoking real services.
Get started with the MATLAB MCP client
This example demonstrates how to easily build an MCP Client in MATLAB to connect with an MCP server and use an LLM to call the server tools. It uses a single tool from a prime sequence MCP server.
Set-up the interface to call OpenAI LLMs
Make sure you get the latest version of the LLM-with-MATLAB repo:
Create a .env file with your OPENAI_API_KEY
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-proj-xxxxx
gitclone("https://github.com/matlab-deep-learning/llms-with-matlab")
addpath("llms-with-matlab")
loadenv '.env'
Build the MCP client
Here is how you can connect to the MCP server endpoint from MATLAB:
endpoint = "https://production-server-demo.mathworks-workshop.com/primeSequence/mcp"; client = mcpHTTPClient(endpoint)
client =
mcpHTTPClient with properties:
Endpoint: "https://production-server-demo.mathworks-workshop.com/primeSequence/mcp"
ServerTools: {[1×1 struct]}
The first step is to discover the tools made available by the MCP server. You can loop to list them all. Here there is only one:
serverTools = client.ServerTools;
for i = 1:length(serverTools)
disp(serverTools{i}.name)
disp(serverTools{i}.description)
disp('---')
end
primeSequence Return the first N primes of the given sequence type. Four sequence types supported: Eisenstein, Balanced, Isolated and Gaussian. ---
Next step is to look up the arguments required to call a tool.
tool1 = serverTools{1};
toolName = tool1.name;
client.ServerTools{1}.inputSchema
client.ServerTools{1}.inputSchema.properties
ans = struct with fields:
n: [1×1 struct]
type: [1×1 struct]
client.ServerTools{1}.inputSchema.properties.n
ans = struct with fields:
type: 'number'
description: 'Length of the generated sequence'
client.ServerTools{1}.inputSchema.properties.type
ans = struct with fields:
type: 'string'
description: 'Name of the sequence to generate'
client.ServerTools{1}.inputSchema.required
ans = 2×1 cell array 'n' 'type'
Integrate the MCP client to the model
The following functions are provided by the LLMs with MATLAB repo. In this example, the OpenAI service is used to provide the Large Language Model.
f = openAIFunction(serverTools)
f =
openAIFunction with properties:
FunctionName: "primeSequence"
Description: "Return the first N primes of the given sequence type. Four sequence types supported: Eisenstein, Balanced, Isolated and Gaussian."
Parameters: [1×1 struct]
model = openAIChat(Model="gpt-5-mini",Tools=f)
model =
openAIChat with properties:
ModelName: "gpt-5-mini"
Temperature: 1
TopP: 1
StopSequences: [0×0 string]
TimeOut: 10
SystemPrompt: []
ResponseFormat: "text"
PresencePenalty: 0
FrequencyPenalty: 0
FunctionNames: "primeSequence"
[~,completeOutput] = generate(model,"generate a sequence of 10 prime numbers")
completeOutput = struct with fields:
role: 'assistant'
content: []
tool_calls: [1×1 struct]
refusal: []
annotations: []
completeOutput.tool_calls
ans = struct with fields:
id: 'call_5TOPVJ5zftW3WWydHQ0fmpyR'
type: 'function'
function: [1×1 struct]
toolRequest = completeOutput.tool_calls(1).function
toolRequest = struct with fields:
name: 'primeSequence'
arguments: '{"n":10,"type":"Eisenstein"}'
output = callTool(client,toolRequest)
output = "[2,5,11,17,23,29,41,47,53,59]"






评论
要发表评论,请点击 此处 登录到您的 MathWorks 帐户或创建一个新帐户。