Highlights from MathWorks Finance Conference 2025

The 2025 MathWorks Finance Conference brought together quants, economists, financial modelers and researchers to explore how MATLAB is shaping the future of finance. Across two days, speakers shared practical applications—from pricing complex instruments to accelerating macroeconomic modelling.
Here are the key highlights.
Day 1: Innovation in Financial Modeling and AI
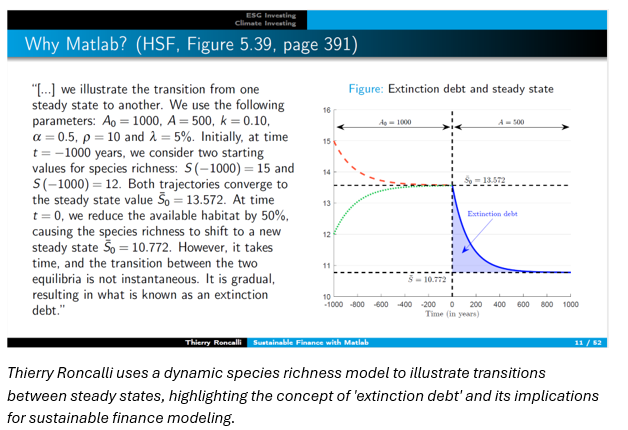
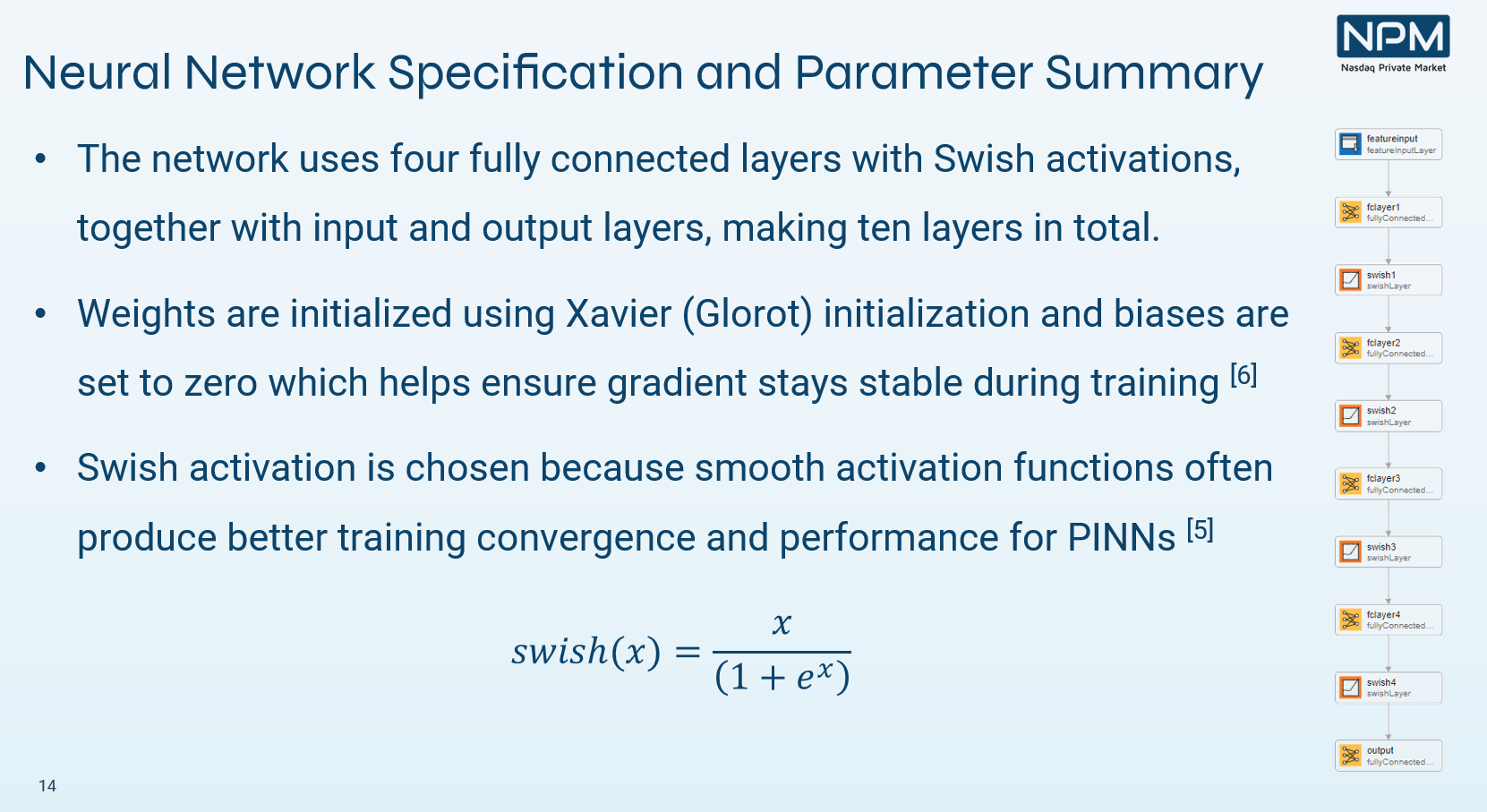
Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) Pricing Using Physics-Informed Neural Networks
Chetan Jadhav, Nasdaq Private Markets
Chetan introduced a pricing method for Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) using Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs). The approach models embedded carry as a stochastic option and trains PINNs on simulated data—offering a transparent method for pricing in illiquid markets.
→ Explore how PINNs outperform traditional models
The Calibration Conundrum: Optimizers and (Joint) Objective Functions
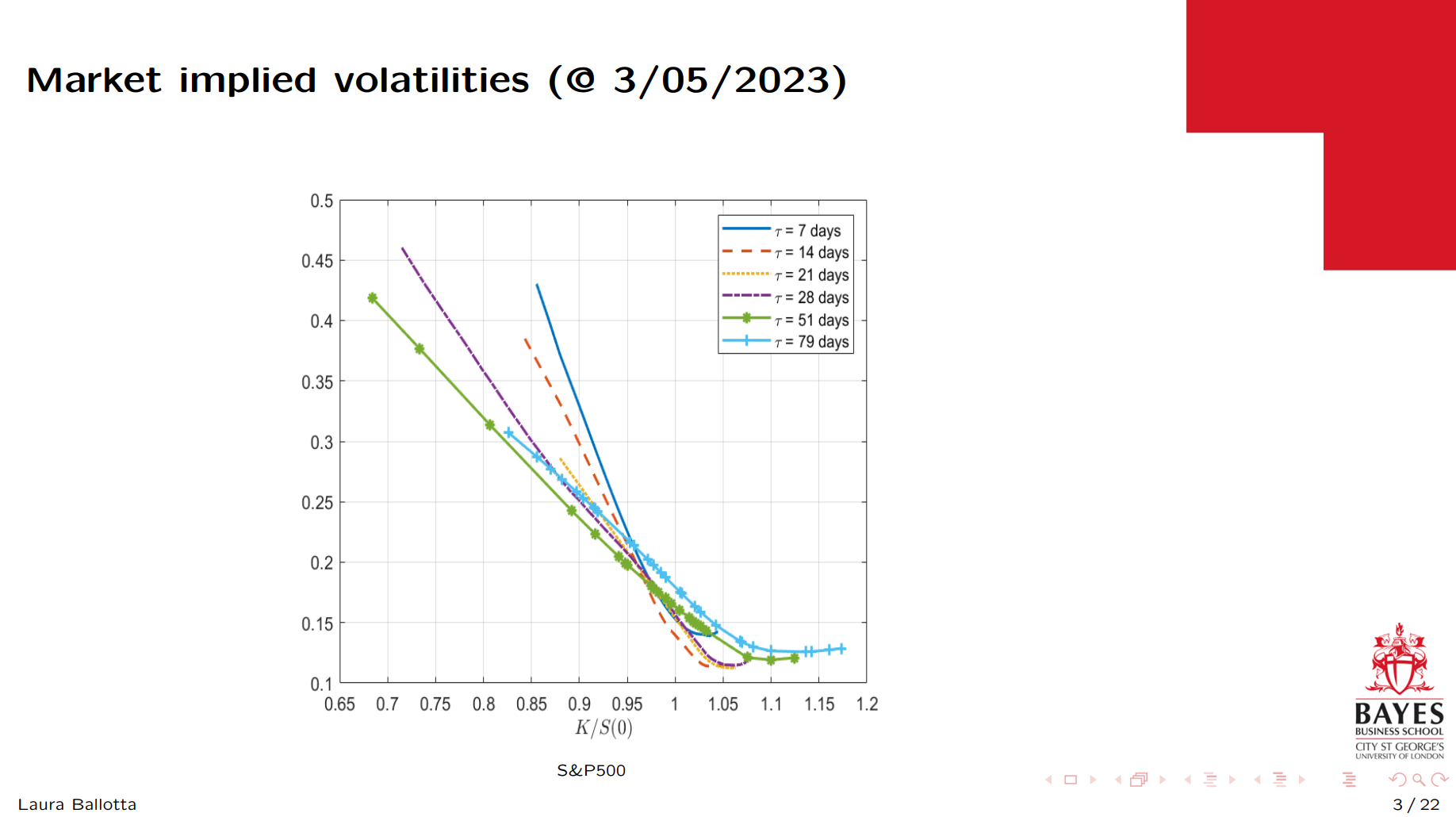
Laura Ballotta, Bayes Business School
Laura examined the challenges of calibrating structured derivatives models. She demonstrated how joint objective functions and optimisers interact, and why calibration is more than just curve fitting—it’s about preserving economic meaning.
→ See how calibration choices affect model behaviour
Using MATLAB with Databricks: Orchestrate, Connect, and Deploy at Scale
Michael Browne, MathWorks
Michael showcased how MATLAB integrates with Databricks to support scalable financial workflows. From JDBC queries, to deploying compiled models on Spark clusters, the session highlighted how MATLAB fits into modern data platforms.
→ Learn how to run MATLAB models in Databricks notebooks
MATLAB Copilot: Accelerate Robust Model Development, Testing, and Validation
Lawrence Johny, MathWorks
Lawrence introduced MATLAB Copilot, a generative AI assistant integrated into MATLAB. Copilot assists with code comprehension, authoring, and validation, enabling faster and more robust model development.
→ Learn about MATLAB Copilot’s editor and chat features
Investment Strategies Ideation using Large-Language Models and Structured Multi-Modal Data
Michael Robbins, Taewan Yoon, and Martina Paez Berru, Columbia University
The team presented a pipeline for generating investment ideas using large-language models and structured multi-modal data. The team used MATLAB to orchestrate data ingestion, vector analysis, and prompting—surfacing niche strategies overlooked by general models.
→ Discover how structured prompting can uncover contrarian ideas
Day 2: Macroeconomic Modelling and Risk Analysis
 David A. Kelley
Federal Reserve Bank of New York
|
 Kaustubh
Reserve Bank of India
|
 Juan Rubio-Ramírez
Emory University
|
 Allan Wright
Central Bank of the Bahamas
|
 Eduard Benet Cerdà
MathWorks
|
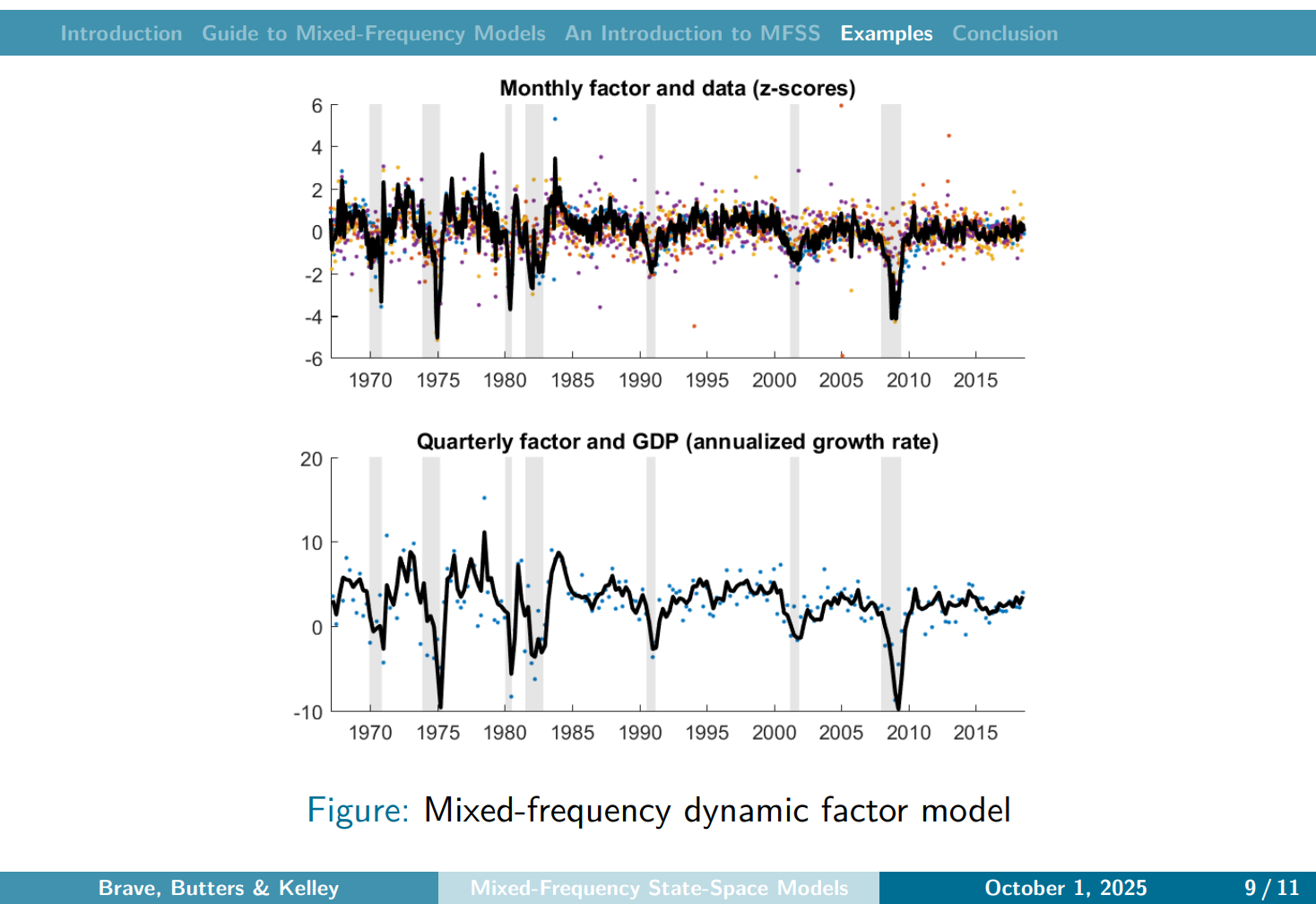
A MATLAB Toolbox for Mixed-Frequency State-Space Models
David Kelley, Federal Reserve Bank of New York
David demonstrated the MFSS toolbox, which simplifies modelling with data observed at different frequencies. David demonstrated how to estimate high-frequency states from mixed inputs, enabling timely forecasts without aggregation loss.
→ See how MFSS handles quarterly and monthly data in this walkthrough
A Multi-Factor Nowcasting Model for India
Kaustubh, Reserve Bank of India
Kaustubh introduced a multi-factor GDP nowcast model using high-frequency indicators. Kaustubh used sigmoid transformations to handle outliers and Kalman filtering to update forecasts in real time.
→ Review the model’s performance across COVID and post-COVID periods
A Gibbs Sampler for Efficient Bayesian Inference Sign-Identified SVARs
Juan Rubio-Ramírez, Emory University
Juan proposed a Gibbs sampler with elliptical slice sampling to estimate large SVARs under tight identification. This method avoids the bottlenecks of accept-reject algorithms and scales to models with many shocks.
→ Learn how this approach improves inference speed
A Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Analysis of a Small Open Economy with Tourism
Allan Wright, Central Bank of The Bahamas
Allan used a DSGE model to simulate the impact of hurricanes on tourism-driven economies. The model showed how climate events drive output and inflation volatility, and how flexible exchange rates can help absorb shocks.
→ View the policy implications for small open economies
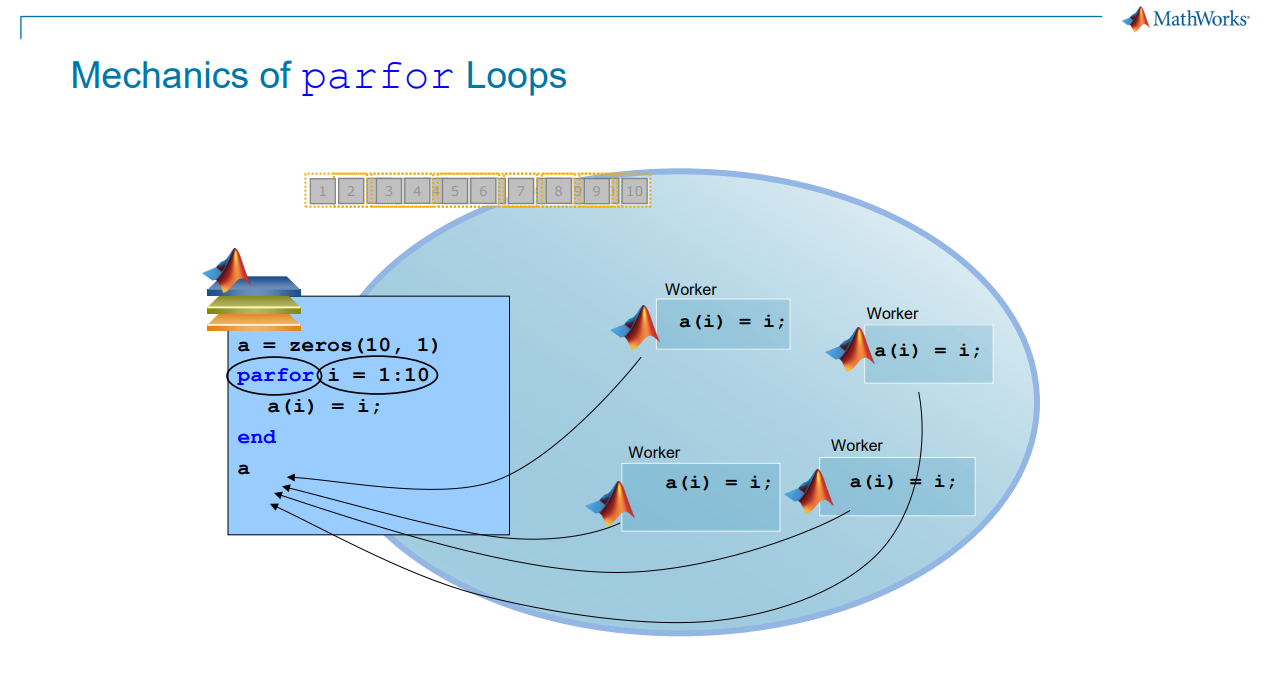
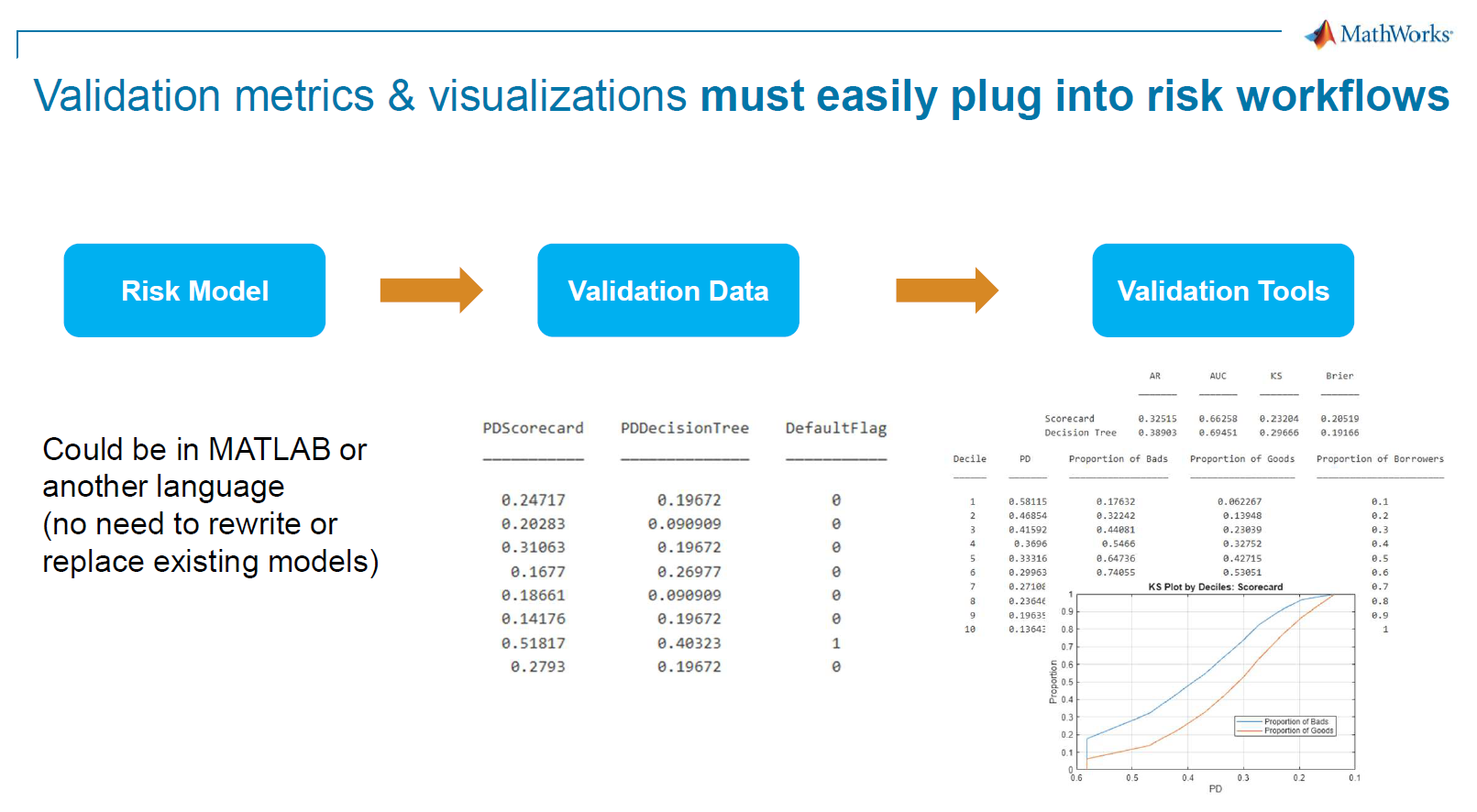
Speed Up Macroeconomic Modeling with MATLAB and Parallel Computing
Eduard Benet Cerdà, MathWorks
Eduard shared practical ways to accelerate macroeconomic models developed in MATLAB, including those based on Dynare. Using MATLAB parallel computing tools—from parfor loops to Experiment Manager—the session covered how to scale estimation tasks across cores and clusters.
→ Find out how to reduce model runtimes from days to hours
If you missed the live sessions, each talk is available on demand. Whether you’re building models, pricing instruments, or forecasting macro trends, the conference offered practical insights for applying MATLAB in finance.













评论
要发表评论,请点击 此处 登录到您的 MathWorks 帐户或创建一个新帐户。