A MATLAB Implementation of the DICE-2023 Model for Climate-Economic Analysis
The DICE (Dynamic Integrated model of Climate and the Economy) model has been a cornerstone for understanding the intricate interplay between economic activity and climate change. A recent publication in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences introduced the DICE-2023 model, an updated version that promises to enhance our analytical capabilities in this crucial field.
The DICE model, originally developed by Nobel laureate William Nordhaus, integrates economic theory with climate science to explore the impacts of policy decisions on climate change and economic growth. The 2023 update incorporates the latest scientific data and methodologies, providing a more robust framework for policymakers and researchers.
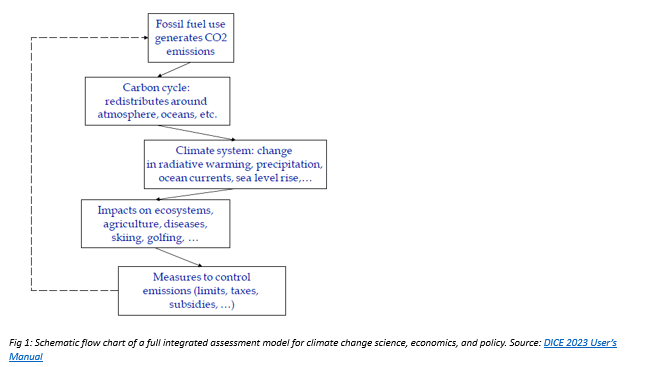
The model now includes revised parameters that reflect the latest scientific understanding of climate sensitivity (improving predictions of temperature changes in response to CO2 emissions). This update is crucial as it aligns the model with the most recent assessments from leading climate research bodies[1][2], ensuring that the projections are both current and accurate.
The economic components of the model have been refined to better account for global economic dynamics and technological advancements. This includes adjustments to growth rates, technological change, and energy efficiency, which are pivotal in modeling long-term economic impacts and the transition to a low-carbon economy.
DICE 2023 offers a broader range of policy scenarios, enabling more comprehensive analysis of potential climate policies and their long-term economic impacts. These scenarios include variations in carbon pricing, technological adoption rates, and international cooperation levels, providing a multifaceted view of possible futures.
MATLAB Implementation
While the original implementation is in GAMS, with an additional implementation in Excel, we recently published a version in MATLAB, implemented by my colleague Eduard Benet Cerdà which allows users to take advantage of all the benefits of MATLAB and the MathWorks ecosystem. This implementation, available on GitHub, offers several benefits:
- Ease of Use: MATLAB’s user-friendly interface allows researchers and policymakers to interact with the model without extensive programming knowledge. The implementation includes a comprehensive set of and functions that simplify the process of running simulations and analyzing results.
- Flexibility: Users can adjust parameters and scenarios to conduct analyses tailored to their research questions or policy objectives. The implementation encourages experimentation and adaptation, making it a versatile tool for a wide range of applications.
- Visualization Tools: MATLAB provides powerful tools for data visualization, enabling users to generate clear and informative graphs and charts that illustrate model outputs. This helps communicate complex results clearly to stakeholders and decision-makers.
- Integration Capabilities: MATLAB’s extensive library of functions and toolboxes allows for seamless integration with other data sources and models, enhancing the scope of analysis. This feature supports interdisciplinary research efforts by enabling the combination of economic, environmental, and social data.
Results of the DICE-2023 Model
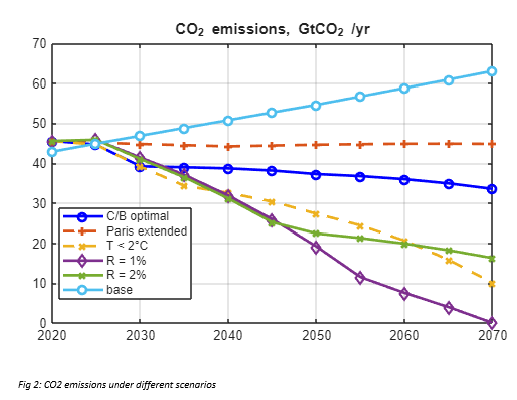
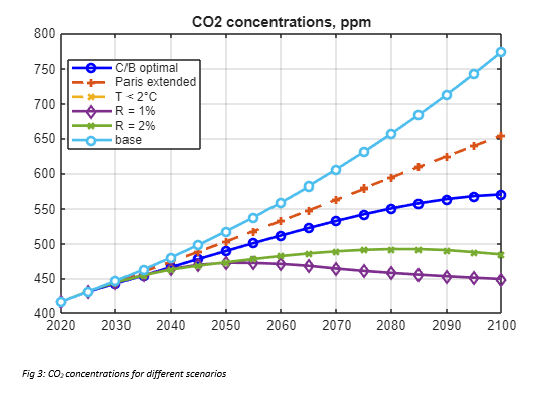
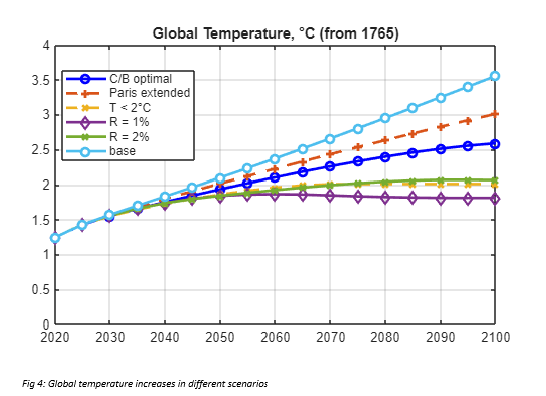
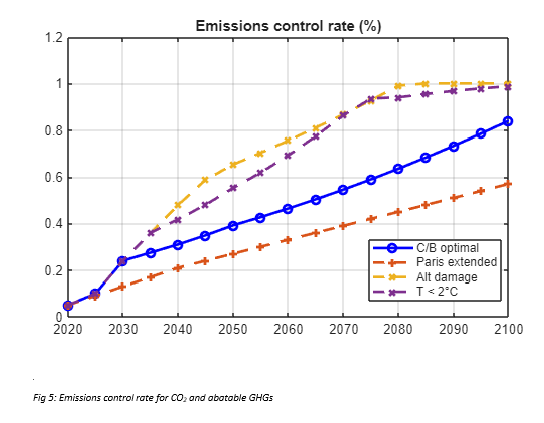
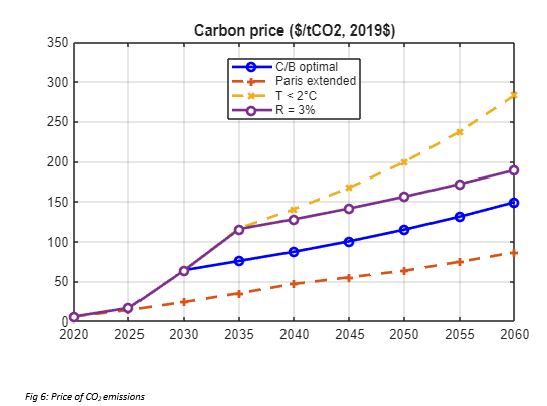
The suite of climate scenarios considered in the study accompanying the model were:
- Baseline: Estimates of current climate policies and trends of current policies as of 2022, extended indefinitely
- Cost-benefit optimal (C/B optimal): Climate change policies maximize economic welfare according to the principles of cost-benefit analysis, with full participation of all nations starting in 2025
- Temperature limited: The C/B optimal policies are undertaken subject to a further constraint that global temperature does not exceed 2C (or other targets) above pre-industrial levels.
- Alternative discount rates: Consider alternatives to the standard approach by setting constant discount rates of 1%, 2%, 3%, 4% or 5% per year
- Alternative damage function (Alt damage): This scenario uses an alternative damage function quantification based on Howard and Sterner (2017) and Howard (2021).
- Paris Accord extended: This scenario assumes that countries meet their objectives in 2030 according to their revised pledges as of summer 2022 and projects slightly less than ½ percentage point increase per year in the control rate from 2030 to 2100.
The following plots demonstrate some of the results from the MATLAB implementation of the DICE-2023 model:
Conclusion
The DICE-2023 model, with its MATLAB implementation, offers a more precise and flexible tool for assessing the economic impacts of climate change and evaluating policy options. Its updated scientific and economic foundations ensure that analyses are grounded in the latest data, providing the necessary level or recency and reliability for decision-makers. Furthermore, the ease of use and adaptability of the MATLAB platform make it accessible to a broader audience, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration.
In conclusion, the DICE-2023 model represents a significant step forward in climate-economic modeling. Its integration into MATLAB not only enhances its analytical power but also democratizes access to this critical tool, empowering more stakeholders to engage in informed climate policy discussions. As we face the pressing challenges of climate change, tools like DICE-2023 are indispensable in guiding effective and sustainable policy decisions.
References
[1] Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
[2] Sherwood, S. C., et al. (2020). “An assessment of Earth’s climate sensitivity using multiple lines of evidence.”








댓글
댓글을 남기려면 링크 를 클릭하여 MathWorks 계정에 로그인하거나 계정을 새로 만드십시오.