What is the most efficient aircraft seating strategy?
Today I am happy to welcome my colleague Ramamurthy Mani for another very interesting study using SimEvents.
Introduction
Recently, I read an article in Wired (TM) magazine that posed a question that I am sure many of you have confronted — what is the most efficient way to get passengers onto an airplane. While this article highlights a theoretical (and deterministic) approach to doing this, I set about trying to model this situation and try some variations of this strategy and others that capture at least a few more elements of randomness in the boarding process.
Generating a queue of passengers
I used MATLAB to generate a queue of passengers utilizing many different boarding strategies. These strategies are shown in the figure below. The most common one used by airlines is the one labeled ‘backToFrontZone’. A colored circle in each plot is more bright than another when that passenger has a higher probability of being in the passenger queue earlier. I use the ‘datasample’ function in MATLAB to generate a sample passenger queue with those weighted probabilities. Each decrease in shade of green represents a 10 fold decrease in probability of a darker shade dot (i.e. passenger) jumping ahead of the brighter shade dot in the queue.
close all; clear all % Boarding types dictate how you want to order passengers for boarding boardingTypes = {'frontToBackZone', 'backToFrontZone', 'random', ... 'alternateRowZone', 'windowToAisleZone', 'windowToAisleAlternateZone'}; %boardingTypes = {'windowToAisleAlternateZone'}; numRows = 20; % Number of rows in the plane numSeatsPerRow = 6; % Number of seats per row crossZoneFactor = 10; % Factor that controls how likely people from different % zones mix. Higher numbers means mixing less likely expRndMeanStowTime = 1/4; % Mean time (mins) for stowing bags expRndMeanGetUpSitTime = 1/6; % Mean time (mins) for getting up and sitting down % when passenger needs to let someone into % their row seatOrders = []; idealOrders = []; for k = 1:length(boardingTypes) fprintf('Generating %s\n', boardingTypes{k}); % Use MATLAB to produce the passenger order [seatOrder, idealOrder] = airseatSetupSim(boardingTypes{k}, 'repeatable', ... numRows, numSeatsPerRow, ... crossZoneFactor, expRndMeanStowTime, ... expRndMeanGetUpSitTime); seatOrders = [seatOrders, seatOrder]; %#ok idealOrders = [idealOrders, idealOrder]; %#ok end airseatDrawBoardingSchemes(boardingTypes, seatOrders);
The six strategies include:
- frontToBackZone: Boarding from front of aircraft to back broken into 4 zones.
- backToFrontZone: Boarding from back of aircraft to front broken into 4 zones.
- random: Boarding happens across the aircraft randomly
- alternateRowZone: Boarding (back to front) is done in four zones and each zone only includes alternate rows.
- windowToAisleZone: Boarding broken into 3 zones as ‘window’, ‘middle’, and ‘aisle’
- windowToAisleAlternateZone: Hybrid of 4 and 5 with 6 zones where alternate rows in window, middle, and aisle are treated as separate zones.

Run simulations
To model the aircraft cabin, I used a model built in SimEvents. SimEvents is discrete-event simulation library for the Simulink platform. To begin, we generate passenger entities and assign them attributes like row and seat number, along with a random amount of time it will take to stow their bag and sit down.

Then using a library I can model one row of seats and then repeat that row as many times as I want to form the cabin. In each row, I use the Attribute Function block, where I can write MATLAB code accessing and modifying attributes of the passenger entities:

I connected 20 of those in series and got interesting results I will describe below.
To make the simulation more visually appealing, I created a custom visualization, using new features available in R2015a. In MATLAB, I created a simevents.CustomObserverInterface object, which I connected to my model using simevents.connectObserver. In the object, I can specify which blocks to observe using getBlocksToObserve, and then I can code any type of visualization in the entityAdvance to be updated when an entity advances.
Here is what the custom observer object looks like. Note that I removed the actual plotting code to help keeping the focus on the SimEvent feature.
classdef airseatViz < simevents.CustomObserverInterface % AIRSEATVIZ Helper class that draws results of airplane seating model. % properties (Access=private) mFig; mPatches = cell(1, 20); mNumRows; mNumSeats; end % --------------------------------------------------------------------- methods (Access=public) function this = airseatViz(numRows, numSeats) this.mNumRows = numRows; this.mNumSeats = numSeats; end function fig = getFigure(this) fig = this.mFig; end function blks = getBlocksToObserve(this) %#ok<MANU> blks1 = find_system('airseat', 'FollowLinks', 'on', ... 'BlockType', 'SingleServer'); blks2 = find_system('airseat', 'FollowLinks', 'on', ... 'BlockType', 'EntitySink'); blks = union(blks1,blks2); end function p = getPace(this) %#ok<MANU> p = 5; end function initialize(this, ~) % Some code to initialiaze the visualization end function entityAdvance(this, entity, ~, to) enStruct = sedb.eninfo(entity); currRow = enStruct.Attributes.CurrentSeatLoc; destRow = enStruct.Attributes.Row; % Some code to update the visualization when entity advance end function entityDestroy(this, entity, ~) % Code to update the isualization when the entity is destroyed end end end % classdef
Here is what the animation looks like for the case where boarding begins at the back of the plane:
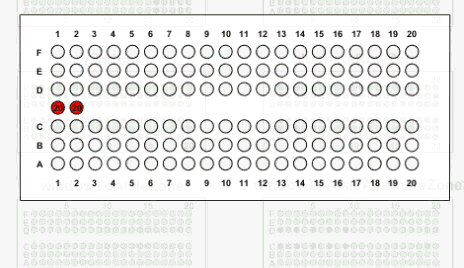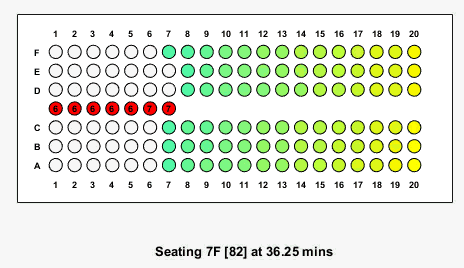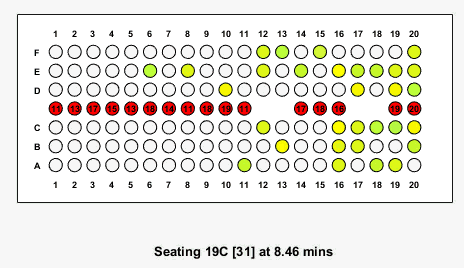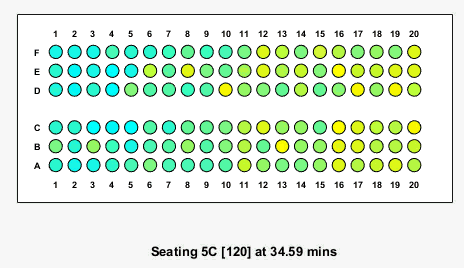
Results
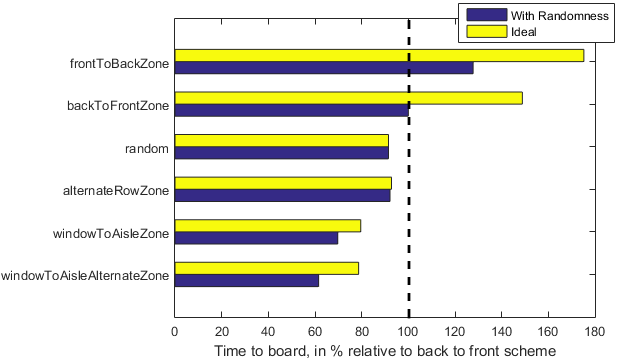
I plotted the results for each scheme, along with the ideal case. I define ideal as a perfectly behaved group that boards exactly in the order prescribed by that scheme with no randomness.
The results do validate that the current process used by airlines can only get worse if they decide to board front to back! I was surprised that some schemes work better than the truly random scheme — but perhaps I should have expected that given the article I started with. It looks like even with the randomness thrown into the deterministic model presented above — represented by the scheme labeled ‘windowToAisleAlternateZone’, it performed the best. Maybe when I am in the airport next time things would have changed for the better?
Here are the results for the six schemes described above, normalized by the back to front scheme, which is the standard used by most companies.
Now it’s your turn
Download Mani’s project here and try coming up with a better boarding scheme.








评论
要发表评论,请点击 此处 登录到您的 MathWorks 帐户或创建一个新帐户。